产品
在前面的章节中,我们以数独游戏为例,得到了一个它的整数规划模型。接着用 Python 实现了一个求解这个模型的类 SudokuModel。但是用起来比较麻烦,模型的输入和输出不直观,需要做相应的转换。
为了求解更方便,我们把 SudokuModel 封装到新的类 SudokuSolver。 它可以自动把数独的输入转化成模型 SudokuModel 的输入,然后把模型的输出转化成数独的输出。
此外,基于模型 SudokuModel 的求解能力,我们实现了一个类 SudokuGenerator,用它来生成数独实例。
最后把生成和求解这两类,封装到一个新的类 SudokuPuzzle 中。这样一来,用户只需要了解 SudokuPuzzle 的用法,而不用了解数独模型以及内部的实现。SudokuPuzzle 就是交付给用户的代码。
虽然 SudokuPuzzle 用起来简单。但是必须用 Python 调用。也就是说,其他语言的开发环境,是不能直接调用的。这就限制了 SudokuPuzzle 的应用场景。为了解决这个问题,我们把它封装成一个网络服务。用户可以通过 http 协议发送请求,从而使用 SudokuPuzzle 的生成和求解功能。
网络服务能解决跨语言调用问题。但是仍然要求用户具备编程能力。为了进一步降低使用门槛,我们可以给它做成一个软件产品,让用户通过一个图形界面进行操作。
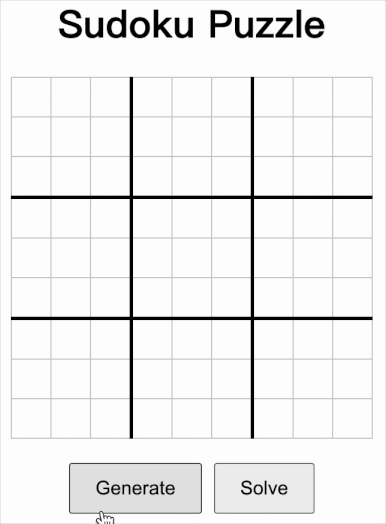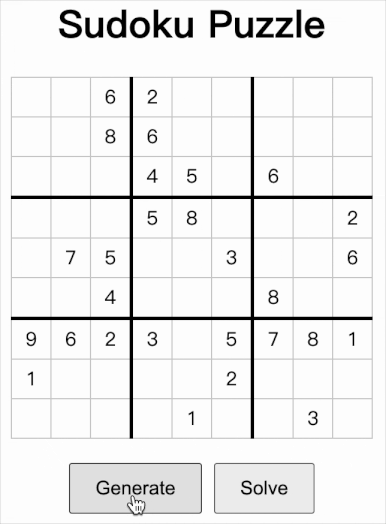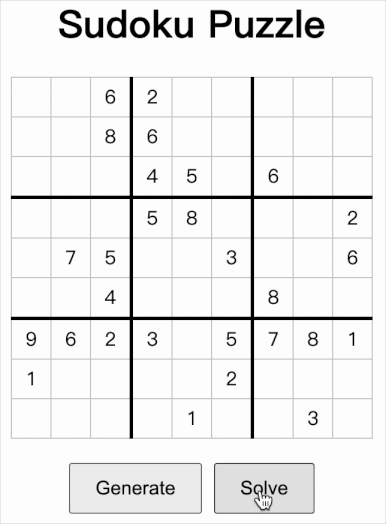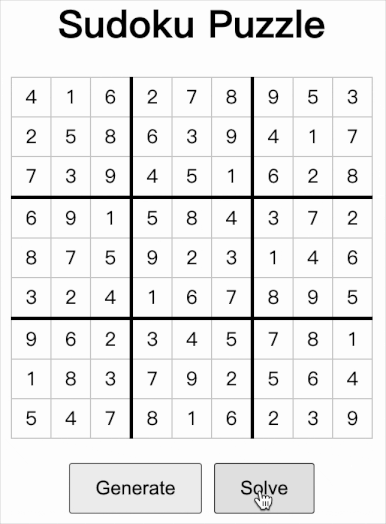
如上图所示,这是网页的前端页面。用户点击 Generate 按钮,页面调用服务 http://127.0.0.1:8000/generate 得到数独实例,页面显示结果;用户再点击 Solve 按钮,页面把数独实例通过 post 方式发送到 http://127.0.0.1:8000/solve,得到计算结果并显示。
接下来讲一下前端页面是如何调用数独服务。
先创建一个 index.html 文件,其中标签 <head> ... </head> 中可以写一些页面信息,比如样式;<body> ... </body> 是页面的主体内容。
<html>
<head>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Sudoku Puzzle</h1>
<table id="sudoku-grid">
</table>
<div class="button-container">
<button id="generate-button">Generate</button>
<button id="solve-button">Solve</button>
</div>
<script>
</script>
</body>
</html>
在标签 <body> ... </body> 中有四个部分:第一个部分是标题 Sudoku Puzzle;第二个部分是用来显示数独游戏的表格 <table> ... </table>,目前是一个定义,没有实际内容;第三个部分是按钮 Generate 和 Solve;前三个部分是页面布局,第四个部分是代码 <script> ... </script>,是页面功能的实现。
在标签 <script> ... </script> 中,要实现如下功能:
- 表格的绘制;
- 点击
Generate按钮,生成数独实例; - 点击
Solve按钮,求解数独实例。
表格绘制这里不做介绍,可以直接看代码。
下面是生成功能的实现。
var board = []; // Declare the board variable outside the event listeners
// Event listener for the "Generate" button
generateButton.addEventListener('click', async () => {
const response = await fetch('http://localhost:8000/generate');
const data = await response.json();
// Extract the board data from the response
board = data.board;
// Populate the table with the received data
for (let i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
const cell = table.rows[i].cells[j];
cell.textContent = board[i][j] === 0 ? '' : board[i][j]; // Display empty string for 0
}
}
});
generateButton.addEventListener 会监听用户的点击操作。如果用户点击按钮,就会执行对应的代码,从接口 http://localhost:8000/generate 中得到数独实例保存在变量 board 中,然后显示到页面。
下面是求解功能的实现。
// Event listener for the "Solve" button
solveButton.addEventListener('click', async () => {
// 1. Prepare the data to send
const data = { board: board };
// 2. Send the data to the solve service
const response = await fetch('http://localhost:8000/solve', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify(data)
});
// 3. Receive the response from the solve service
const solvedData = await response.json();
const solvedBoard = solvedData.solution;
const status = solvedData.status;
if (status === 'SOLVED') {
// 4. Display the solved Sudoku on the table
for (let i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
const cell = table.rows[i].cells[j];
cell.textContent = solvedBoard[i][j] === 0 ? '' : solvedBoard[i][j];
}
}
}
});
变量 board 代表一个数独实例。把 board 封装成 json 格式,通过 post 方式发送给 http://localhost:8000/solve 求解,最后把结果显示在页面上。
完整代码请参考 codes/application/web/index.html
Last updated 04 May 2025, 10:38 +0800 .